Table of Contents
Could this experimental treatment reverse damage caused by a heart assault? The heart muscle counts on a constant circulation of oxygen-rich blood to nourish it and keep it pumping. During a cardiac arrest, that blood flow is disrupted by a blockage in an artery. Without blood, the location of heart fed by the influenced artery starts to die and mark cells kinds in the area.
Though the heart is a tough organ, the broken parts end up being unable to pump blood as successfully as they once could. People that have actually had a cardiovascular disease therefore may face a life time of maintenance therapymedications and other therapies focused on avoiding an additional heart strike and aiding the heart work a lot more effectively.
In a research study published last February in The Lancet, researchers treated 17 heart strike clients with an infusion of stem cells taken from their own hearts. A year after the treatment, the quantity of mark tissue had actually shrunk by about 50%. These outcomes sound dramatic, but are they an indication that we're getting near to perfecting this therapy? "This is an area where, relying on which detective you ask, you can obtain exceptionally various solutions," says Dr.
"The area is young. Some research studies reveal only modest or no improvement in heart feature, but others have actually shown significantly boosted feature," he claims. "We're waiting to see if various other doctors can also accomplish actually great results in various other people." Studies are creating such different results in component because scientists are taking various approaches to harvesting and using stem cells.
Much more long-term trials are needed to determine the duty stem cell therapy will have in treating heart disease. When might stem cell therapy come to be a basic therapy for damaged heart muscle mass? As of currently, stem cell treatment is offered only to individuals that get involved in a research test.
Cardiovascular disease is a significant health and wellness issue and affects millions of people each year. According to the Centers for Condition Control (CDC), heart illness kills a single person every 33 seconds in the United States and is the leading reason of fatality for males and females throughout most racial and ethnic groups.
New hope for Peripheral Artery Disease via regenerative medicine
Standard therapies (medicine, lifestyle modifications, and surgery) can aid people take care of symptoms and slow down the progress of heart problem. What about after a heart-related event? They don't help when it comes to fixing broken heart cells. Heart stem cells assurance to change that situation. These cells have significant potential when it involves heart regrowth and healing.

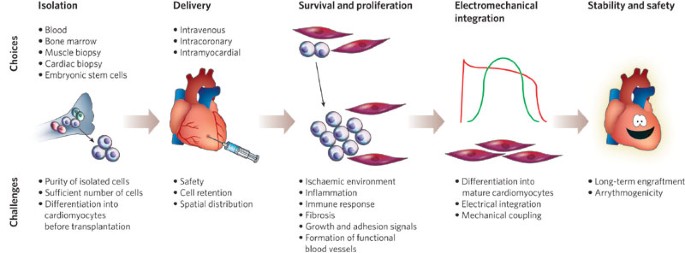
(divide to make even more stem cells) and differentiate into cardiomyocytes (the cells within the muscular tissues that make your heart agreement) for myocardial repair service. That's especially real after occasions like a heart strike, where parts of the heart muscle may pass away due to a lack of blood flow.
(the formation of new blood vessels) to recover blood circulation. And also, heart stem cells aid lower swelling, making it simpler for cells to heal and restore.
Once heart cells are lost, your body typically can not restore them.
Some currently reveal favorable outcomes, like enhanced heart feature and reduced scar cells. When it pertains to heart regeneration, scientists are studying a number of kinds of stem cells. Of program, each has its very own advantages and disadvantages:: These cells can develop into any sort of cell, so they're highly functional.
Regenerative injections targeting Heart Disease with minimal downtime
: iPSCs are produced by reprogramming adult cells to imitate embryonic stem cells. They give patient-specific therapy, which decreases the risk of rejection.: MSCs are much easier to collect, particularly from bone marrow or fat cells, and since they're patient-specific, there's less threat of being rejected. They additionally minimize swelling and speed up recovery.
Navigation
Latest Posts
What to know about how stem cells help with Heart Failure
Breakthrough option for High Blood Pressure using stem cells
Leading providers of stem cell therapy targeting Peripheral Artery Disease